职责链模式 (Chain of Responsibility Pattern) - 请求的链式处理
避免请求发送者与接收者耦合在一起,让多个对象都有可能接收请求,将这些对象连接成一条链,并且沿着这条链传递请求,直到有对象处理它为止。职责链模式是一种对象行为型模式。
职责链模式并不创建职责链,职责链的创建工作必须由系统的其他部分来完成,一般是在使用该职责链的客户端中创建职责链。
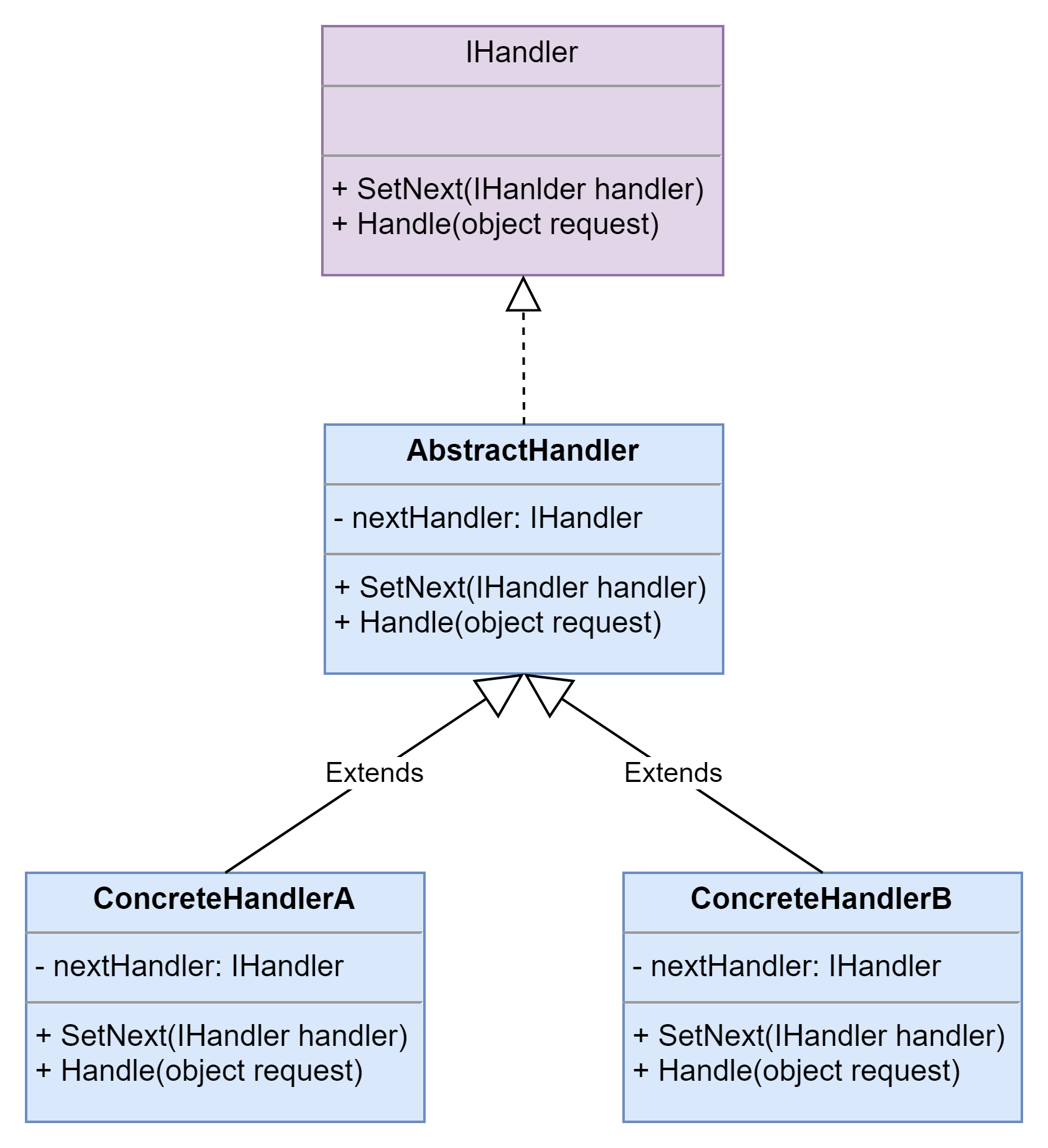
结构图
- AbstractHandler(抽象处理者):它定义了一个处理请求的接口,一般设计为抽象类,由于不同的具体处理者处理请求的方式不同,因此在其中定义了抽象请求处理方法。因为每一个处理者的下家还是一个处理者,因此在抽象处理者中定义了一个抽象处理者类型的对象(如结构图中的nextHandler),作为其对下家的引用。通过该引用,处理者可以连成一条链。
- ConcreteHandler(具体处理者):它是抽象处理者的子类,可以处理用户请求,在具体处理者类中实现了抽象处理者中定义的抽象请求处理方法,在处理请求之前需要进行判断,看是否有相应的处理权限,如果可以处理请求就处理它,否则将请求转发给后继者;在具体处理者中可以访问链中下一个对象,以便请求的转发。
在职责链模式里,很多对象由每一个对象对其下家的引用而连接起来形成一条链。请求在这个链上传递,直到链上的某一个对象决定处理此请求。发出这个请求的客户端并不知道链上的哪一个对象最终处理这个请求,这使得系统可以在不影响客户端的情况下动态地重新组织链和分配责任。
示例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace DesignPatterns.ChainOfResponsibility
{
// The Handler interface declares a method for building the chain of
// handlers. It also declares a method for executing a request.
public interface IHandler
{
IHandler SetNext(IHandler handler);
object Handle(object request);
}
// The default chaining behavior can be implemented inside a base handler
// class.
abstract class AbstractHandler : IHandler
{
private IHandler _nextHandler;
public IHandler SetNext(IHandler handler)
{
this._nextHandler = handler;
// Returning a handler from here will let us link handlers in a
// convenient way like this:
// monkey.SetNext(squirrel).SetNext(dog);
return handler;
}
public virtual object Handle(object request)
{
if (this._nextHandler != null)
{
return this._nextHandler.Handle(request);
}
else
{
return null;
}
}
}
class MonkeyHandler : AbstractHandler
{
public override object Handle(object request)
{
if ((request as string) == "Banana")
{
return $"Monkey: I'll eat the {request.ToString()}.\n";
}
else
{
return base.Handle(request);
}
}
}
class SquirrelHandler : AbstractHandler
{
public override object Handle(object request)
{
if (request.ToString() == "Nut")
{
return $"Squirrel: I'll eat the {request.ToString()}.\n";
}
else
{
return base.Handle(request);
}
}
}
class DogHandler : AbstractHandler
{
public override object Handle(object request)
{
if (request.ToString() == "MeatBall")
{
return $"Dog: I'll eat the {request.ToString()}.\n";
}
else
{
return base.Handle(request);
}
}
}
class Client
{
// The client code is usually suited to work with a single handler. In
// most cases, it is not even aware that the handler is part of a chain.
public static void ClientCode(AbstractHandler handler)
{
foreach (var food in new List<string> { "Nut", "Banana", "Cup of coffee" })
{
Console.WriteLine($"Client: Who wants a {food}?");
var result = handler.Handle(food);
if (result != null)
{
Console.Write($" {result}");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($" {food} was left untouched.");
}
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// The other part of the client code constructs the actual chain.
var monkey = new MonkeyHandler();
var squirrel = new SquirrelHandler();
var dog = new DogHandler();
monkey.SetNext(squirrel).SetNext(dog);
// The client should be able to send a request to any handler, not
// just the first one in the chain.
Console.WriteLine("Chain: Monkey > Squirrel > Dog\n");
Client.ClientCode(monkey);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Subchain: Squirrel > Dog\n");
Client.ClientCode(squirrel);
}
}
}运行结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Chain: Monkey > Squirrel > Dog
Client: Who wants a Nut?
Squirrel: I'll eat the Nut.
Client: Who wants a Banana?
Monkey: I'll eat the Banana.
Client: Who wants a Cup of coffee?
Cup of coffee was left untouched.
Subchain: Squirrel > Dog
Client: Who wants a Nut?
Squirrel: I'll eat the Nut.
Client: Who wants a Banana?
Banana was left untouched.
Client: Who wants a Cup of coffee?
Cup of coffee was left untouched.
总结
职责链模式通过建立一条链来组织请求的处理者,请求将沿着链进行传递,请求发送者无须知道请求在何时、何处以及如何被处理,实现了请求发送者与处理者的解耦。
优点
- 职责链模式使得一个对象无须知道是其他哪一个对象处理其请求,对象仅需知道该请求会被处理即可,接收者和发送者都没有对方的明确信息,且链中的对象不需要知道链的结构,由客户端负责链的创建,降低了系统的耦合度。
- 请求处理对象仅需维持一个指向其后继者的引用,而不需要维持它对所有的候选处理者的引用,可简化对象的相互连接。
- 在给对象分派职责时,职责链可以给我们更多的灵活性,可以通过在运行时对该链进行动态的增加或修改来增加或改变处理一个请求的职责。
- 在系统中增加一个新的具体请求处理者时无须修改原有系统的代码,只需要在客户端重新建链即可,从这一点来看是符合“开闭原则”的。
缺点
- 由于一个请求没有明确的接收者,那么就不能保证它一定会被处理,该请求可能一直到链的末端都得不到处理;一个请求也可能因职责链没有被正确配置而得不到处理。
- 对于比较长的职责链,请求的处理可能涉及到多个处理对象,系统性能将受到一定影响,而且在进行代码调试时不太方便。
- 如果建链不当,可能会造成循环调用,将导致系统陷入死循环。
适用场景
- 有多个对象可以处理同一个请求,具体哪个对象处理该请求待运行时刻再确定,客户端只需将请求提交到链上,而无须关心请求的处理对象是谁以及它是如何处理的。
- 在不明确指定接收者的情况下,向多个对象中的一个提交一个请求。
- 可动态指定一组对象处理请求,客户端可以动态创建职责链来处理请求,还可以改变链中处理者之间的先后次序。
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.