备忘录模式 (Memento Pattern) - 撤销功能的实现
在不破坏封装的前提下,捕获一个对象的内部状态,并在该对象之外保存这个状态,这样可以在以后将对象恢复到原先保存的状态。它是一种对象行为型模式,其别名为Token。
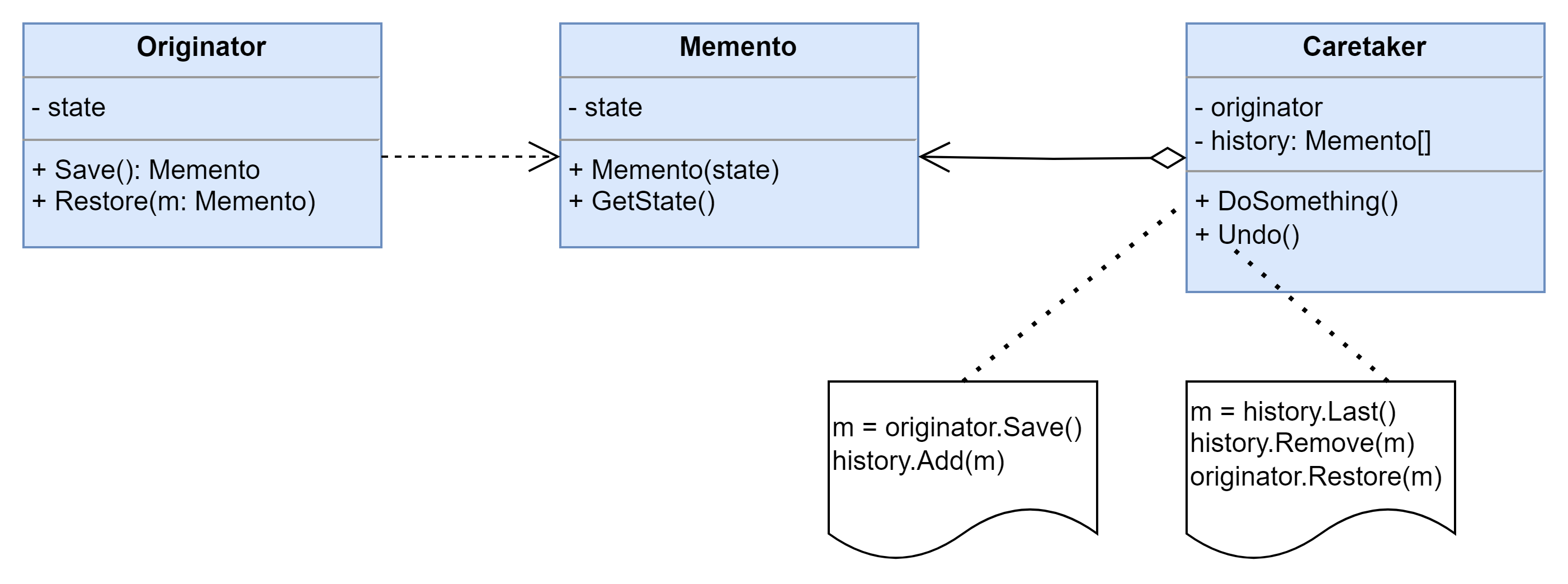
结构图
- Originator(原发器):它是一个普通类,可以创建一个备忘录,并存储它的当前内部状态,也可以使用备忘录来恢复其内部状态,一般将需要保存内部状态的类设计为原发器。
- Memento(备忘录):存储原发器的内部状态,根据原发器来决定保存哪些内部状态。备忘录的设计一般可以参考原发器的设计,根据实际需要确定备忘录类中的属性。需要注意的是,除了原发器本身与负责人类之外,备忘录对象不能直接供其他类使用,原发器的设计在不同的编程语言中实现机制会有所不同。
- Caretaker(负责人):负责人又称为管理者,它负责保存备忘录,但是不能对备忘录的内容进行操作或检查。在负责人类中可以存储一个或多个备忘录对象,它只负责存储对象,而不能修改对象,也无须知道对象的实现细节。
示例
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading;
namespace DesignPatterns.Memento
{
// The Originator holds some important state that may change over time. It
// also defines a method for saving the state inside a memento and another
// method for restoring the state from it.
class Originator
{
// For the sake of simplicity, the originator's state is stored inside a
// single variable.
private string _state;
public Originator(string state)
{
this._state = state;
Console.WriteLine("Originator: My initial state is: " + state);
}
// The Originator's business logic may affect its internal state.
// Therefore, the client should backup the state before launching
// methods of the business logic via the save() method.
public void DoSomething()
{
Console.WriteLine("Originator: I'm doing something important.");
this._state = this.GenerateRandomString(30);
Console.WriteLine($"Originator: and my state has changed to: {_state}");
}
private string GenerateRandomString(int length = 10)
{
string allowedSymbols = "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
string result = string.Empty;
while (length > 0)
{
result += allowedSymbols[new Random().Next(0, allowedSymbols.Length)];
Thread.Sleep(12);
length--;
}
return result;
}
// Saves the current state inside a memento.
public IMemento Save()
{
return new ConcreteMemento(this._state);
}
// Restores the Originator's state from a memento object.
public void Restore(IMemento memento)
{
if (!(memento is ConcreteMemento))
{
throw new Exception("Unknown memento class " + memento.ToString());
}
this._state = memento.GetState();
Console.Write($"Originator: My state has changed to: {_state}");
}
}
// The Memento interface provides a way to retrieve the memento's metadata,
// such as creation date or name. However, it doesn't expose the
// Originator's state.
public interface IMemento
{
string GetName();
string GetState();
DateTime GetDate();
}
// The Concrete Memento contains the infrastructure for storing the
// Originator's state.
class ConcreteMemento : IMemento
{
private string _state;
private DateTime _date;
public ConcreteMemento(string state)
{
this._state = state;
this._date = DateTime.Now;
}
// The Originator uses this method when restoring its state.
public string GetState()
{
return this._state;
}
// The rest of the methods are used by the Caretaker to display
// metadata.
public string GetName()
{
return $"{this._date} / ({this._state.Substring(0, 9)})...";
}
public DateTime GetDate()
{
return this._date;
}
}
// The Caretaker doesn't depend on the Concrete Memento class. Therefore, it
// doesn't have access to the originator's state, stored inside the memento.
// It works with all mementos via the base Memento interface.
class Caretaker
{
private List<IMemento> _mementos = new List<IMemento>();
private Originator _originator = null;
public Caretaker(Originator originator)
{
this._originator = originator;
}
public void Backup()
{
Console.WriteLine("\nCaretaker: Saving Originator's state...");
this._mementos.Add(this._originator.Save());
}
public void Undo()
{
if (this._mementos.Count == 0)
{
return;
}
var memento = this._mementos.Last();
this._mementos.Remove(memento);
Console.WriteLine("Caretaker: Restoring state to: " + memento.GetName());
try
{
this._originator.Restore(memento);
}
catch (Exception)
{
this.Undo();
}
}
public void ShowHistory()
{
Console.WriteLine("Caretaker: Here's the list of mementos:");
foreach (var memento in this._mementos)
{
Console.WriteLine(memento.GetName());
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Client code.
Originator originator = new Originator("Super-duper-super-puper-super.");
Caretaker caretaker = new Caretaker(originator);
caretaker.Backup();
originator.DoSomething();
caretaker.Backup();
originator.DoSomething();
caretaker.Backup();
originator.DoSomething();
Console.WriteLine();
caretaker.ShowHistory();
Console.WriteLine("\nClient: Now, let's rollback!\n");
caretaker.Undo();
Console.WriteLine("\n\nClient: Once more!\n");
caretaker.Undo();
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
}运行结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
Originator: My initial state is: Super-duper-super-puper-super.
Caretaker: Saving Originator's state...
Originator: I'm doing something important.
Originator: and my state has changed to: oGyQIIatlDDWNgYYqJATTmdwnnGZQj
Caretaker: Saving Originator's state...
Originator: I'm doing something important.
Originator: and my state has changed to: jBtMDDWogzzRJbTTmEwOOhZrjjBULe
Caretaker: Saving Originator's state...
Originator: I'm doing something important.
Originator: and my state has changed to: exoHyyRkbuuNEXOhhArKccUmexPPHZ
Caretaker: Here's the list of mementos:
12.06.2018 15:52:45 / (Super-dup...)
12.06.2018 15:52:46 / (oGyQIIatl...)
12.06.2018 15:52:46 / (jBtMDDWog...)
Client: Now, let's rollback!
Caretaker: Restoring state to: 12.06.2018 15:52:46 / (jBtMDDWog...)
Originator: My state has changed to: jBtMDDWogzzRJbTTmEwOOhZrjjBULe
Client: Once more!
Caretaker: Restoring state to: 12.06.2018 15:52:46 / (oGyQIIatl...)
Originator: My state has changed to: oGyQIIatlDDWNgYYqJATTmdwnnGZQj
总结
备忘录模式在很多软件的使用过程中普遍存在,但是在应用软件开发中,它的使用频率并不太高,因为现在很多基于窗体和浏览器的应用软件并没有提供撤销操作。如果需要为软件提供撤销功能,备忘录模式无疑是一种很好的解决方案。在一些字处理软件、图像编辑软件、数据库管理系统等软件中备忘录模式都得到了很好的应用。
优点
- 它提供了一种状态恢复的实现机制,使得用户可以方便地回到一个特定的历史步骤,当新的状态无效或者存在问题时,可以使用暂时存储起来的备忘录将状态复原。
- 备忘录实现了对信息的封装,一个备忘录对象是一种原发器对象状态的表示,不会被其他代码所改动。备忘录保存了原发器的状态,采用列表、堆栈等集合来存储备忘录对象可以实现多次撤销操作。
缺点
资源消耗过大,如果需要保存的原发器类的成员变量太多,就不可避免需要占用大量的存储空间,每保存一次对象的状态都需要消耗一定的系统资源。
适用场景
- 保存一个对象在某一个时刻的全部状态或部分状态,这样以后需要时它能够恢复到先前的状态,实现撤销操作。
- 防止外界对象破坏一个对象历史状态的封装性,避免将对象历史状态的实现细节暴露给外界对象。
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.