代理模式 (Proxy Pattern)
给某一个对象提供一个代理或占位符,并由代理对象来控制对原对象的访问。它是一种对象结构型模式。
在代理模式中引入了一个新的代理对象,代理对象在客户端对象和目标对象之间起到中介的作用,它去掉客户不能看到的内容和服务或者增添客户需要的额外的新服务。
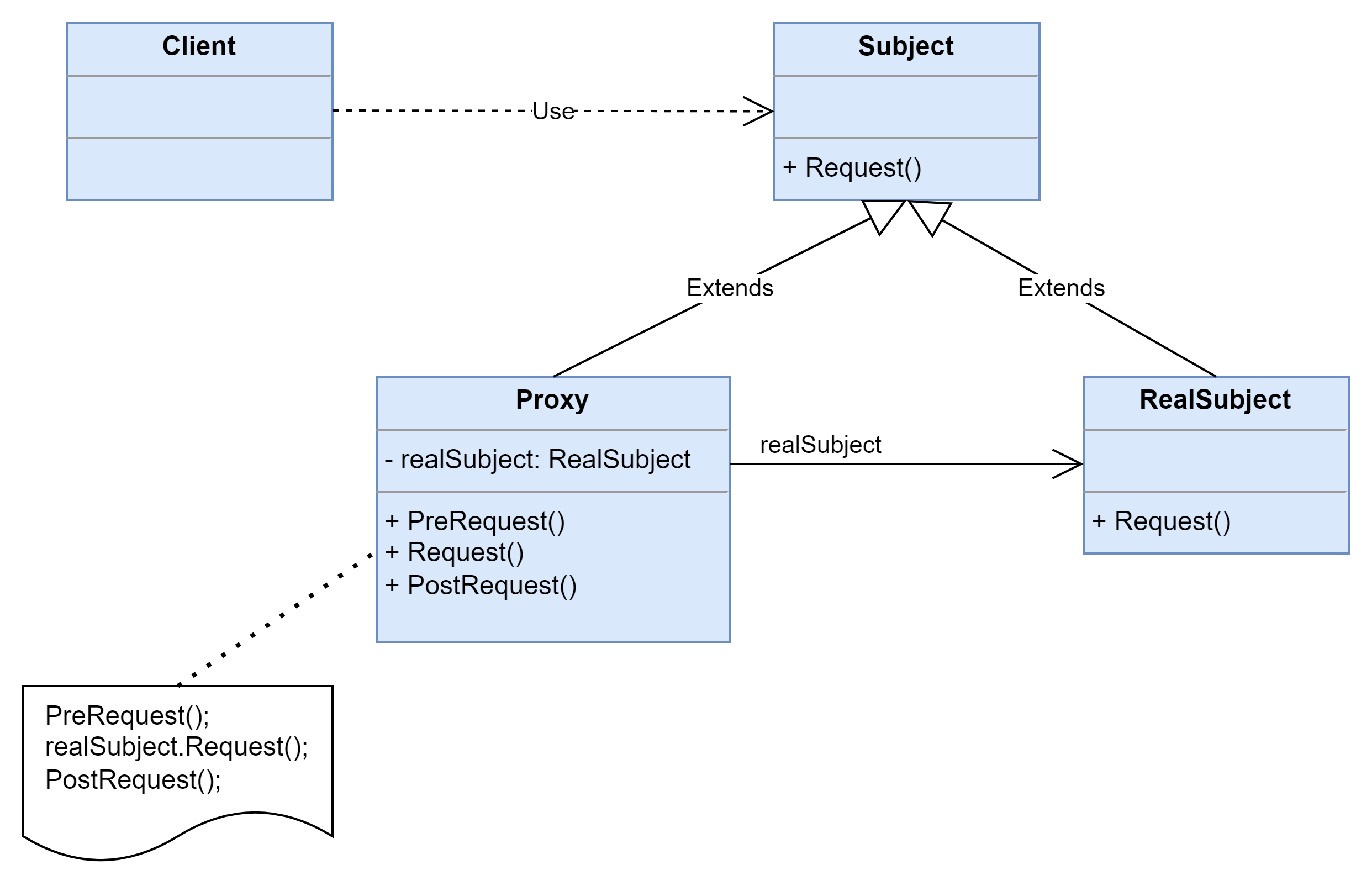
结构图
- Subject(抽象主题角色):它声明了真实主题和代理主题的共同接口,这样一来在任何使用真实主题的地方都可以使用代理主题,客户端通常需要针对抽象主题角色进行编程。
- Proxy(代理主题角色):它包含了对真实主题的引用,从而可以在任何时候操作真实主题对象;在代理主题角色中提供一个与真实主题角色相同的接口,以便在任何时候都可以替代真实主题;代理主题角色还可以控制对真实主题的使用,负责在需要的时候创建和删除真实主题对象,并对真实主题对象的使用加以约束。通常,在代理主题角色中,客户端在调用所引用的真实主题操作之前或之后还需要执行其他操作,而不仅仅是单纯调用真实主题对象中的操作。
- RealSubject(真实主题角色):它定义了代理角色所代表的真实对象,在真实主题角色中实现了真实的业务操作,客户端可以通过代理主题角色间接调用真实主题角色中定义的操作。
示例
using System;
namespace DesignPatterns.Proxy
{
// The Subject interface declares common operations for both RealSubject and
// the Proxy. As long as the client works with RealSubject using this
// interface, you'll be able to pass it a proxy instead of a real subject.
public interface ISubject
{
void Request();
}
// The RealSubject contains some core business logic. Usually, RealSubjects
// are capable of doing some useful work which may also be very slow or
// sensitive - e.g. correcting input data. A Proxy can solve these issues
// without any changes to the RealSubject's code.
class RealSubject : ISubject
{
public void Request()
{
Console.WriteLine("RealSubject: Handling Request.");
}
}
// The Proxy has an interface identical to the RealSubject.
class Proxy : ISubject
{
private RealSubject _realSubject;
public Proxy(RealSubject realSubject)
{
this._realSubject = realSubject;
}
// The most common applications of the Proxy pattern are lazy loading,
// caching, controlling the access, logging, etc. A Proxy can perform
// one of these things and then, depending on the result, pass the
// execution to the same method in a linked RealSubject object.
public void Request()
{
if (this.CheckAccess())
{
this._realSubject.Request();
this.LogAccess();
}
}
public bool CheckAccess()
{
// Some real checks should go here.
Console.WriteLine("Proxy: Checking access prior to firing a real request.");
return true;
}
public void LogAccess()
{
Console.WriteLine("Proxy: Logging the time of request.");
}
}
public class Client
{
// The client code is supposed to work with all objects (both subjects
// and proxies) via the Subject interface in order to support both real
// subjects and proxies. In real life, however, clients mostly work with
// their real subjects directly. In this case, to implement the pattern
// more easily, you can extend your proxy from the real subject's class.
public void ClientCode(ISubject subject)
{
// ...
subject.Request();
// ...
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Client client = new Client();
Console.WriteLine("Client: Executing the client code with a real subject:");
RealSubject realSubject = new RealSubject();
client.ClientCode(realSubject);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine("Client: Executing the same client code with a proxy:");
Proxy proxy = new Proxy(realSubject);
client.ClientCode(proxy);
}
}
}运行结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Client: Executing the client code with a real subject:
RealSubject: Handling Request.
Client: Executing the same client code with a proxy:
Proxy: Checking access prior to firing a real request.
RealSubject: Handling Request.
Proxy: Logging the time of request.
总结
代理模式是常用的结构型设计模式之一,它为对象的间接访问提供了一个解决方案,可以对对象的访问进行控制。代理模式类型较多,其中远程代理、虚拟代理、保护代理等在软件开发中应用非常广泛。
优点
- 能够协调调用者和被调用者,在一定程度上降低了系统的耦合度。
- 客户端可以针对抽象主题角色进行编程,增加和更换代理类无须修改源代码,符合开闭原则,系统具有较好的灵活性和可扩展性。
此外,不同类型的代理模式也具有独特的优点,例如:
- 远程代理为位于两个不同地址空间对象的访问提供了一种实现机制,可以将一些消耗资源较多的对象和操作移至性能更好的计算机上,提高系统的整体运行效率。
- 虚拟代理通过一个消耗资源较少的对象来代表一个消耗资源较多的对象,可以在一定程度上节省系统的运行开销。
- 缓冲代理为某一个操作的结果提供临时的缓存存储空间,以便在后续使用中能够共享这些结果,优化系统性能,缩短执行时间。
- 保护代理可以控制对一个对象的访问权限,为不同用户提供不同级别的使用权限。
缺点
- 由于在客户端和真实主题之间增加了代理对象,因此有些类型的代理模式可能会造成请求的处理速度变慢,例如保护代理。
- 实现代理模式需要额外的工作,而且有些代理模式的实现过程较为复杂,例如远程代理。
适用场景
- 当客户端对象需要访问远程主机中的对象时可以使用远程代理。
- 当需要用一个消耗资源较少的对象来代表一个消耗资源较多的对象,从而降低系统开销、缩短运行时间时可以使用虚拟代理,例如一个对象需要很长时间才能完成加载时。
- 当需要为某一个被频繁访问的操作结果提供一个临时存储空间,以供多个客户端共享访问这些结果时可以使用缓冲代理。通过使用缓冲代理,系统无须在客户端每一次访问时都重新执行操作,只需直接从临时缓冲区获取操作结果即可。
- 当需要控制对一个对象的访问,为不同用户提供不同级别的访问权限时可以使用保护代理。
- 当需要为一个对象的访问(引用)提供一些额外的操作时可以使用智能引用代理。
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.